İnventory Management System
What is inventory management and why having the right tools is important? The Smartic Pro inventory management system (IMS) ensures that the right quantity of stock is being held to meet customer needs without causing overstock or stock shortages. Smartic Pro This system is important for effective management, cost reduction, and increasing customer satisfaction. This article aims to cover widely used components, advantages, hurdles faced, and dos and don’ts of inventory management systems, helping to unlock the full potential and execution of these systems.
What is a Inventory Management System?
Inventory Management System is a software application that allows organizations to manage their inventory and stock levels, orders, sales and deliveries. Smartic Pro It gives a live view of stock status to make sure buildings stock levels are well properly planned order management, and supply chain efficiency. An IMS can be independent system or part of a large ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system.
Features of An Inventory Management System
Real-Time Inventory Tracking: The primary function of an IMS is to track inventory levels in real time. Smartic Pro This involves tracking stock levels, locations, and movements within warehouses and across various facilities.
Order Management: An IMS assists in managing incoming and outgoing orders, making sure that stock levels are updated appropriately. Order processing, fulfillment, and tracking are all a part of this.
Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting is the key to Smartic Pro inventory management. An IMS analyzes past data along with predictive analytics to forecast demand, helping enterprises maintain adequate stock levels.
Replenishment Planning: it decides when the stock should be reordered according to the current stock levels and anticipated demand. This ensures that you never overstock and run out of stock.
Example 4: Supplier Management — An IMS manages supplier relationships and procurement processes. It monitors metrics such as supplier performance, lead times, and order history to facilitate replenishment of stock based on its demand.
Reporting and Analytics: In-depth reports and analytics help monitor inventory performance, identify trends, and pinpoint areas for improvement. Smartic Pro This enable companies to take data-based actions to improve inventory management.
Integration with Barcode and RFID: Many solutions for IMS integrate with other technological systems such as barcode scanning and RFID to help streamline inventory track of items and minimize mistakes of manual entry. These technologies offer efficient and accurate means of managing stock.
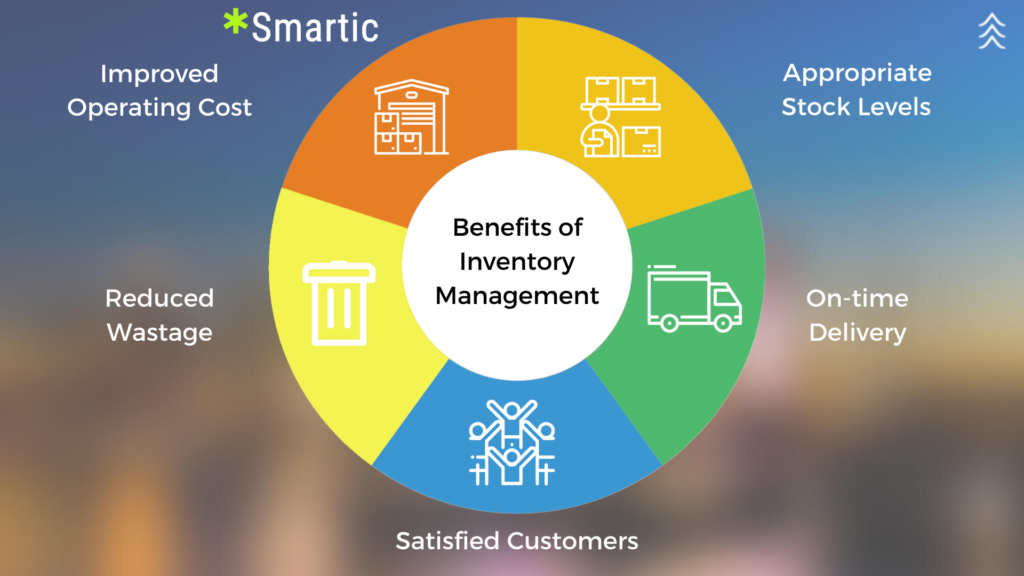
Advantages of an Inventory Management System
Better Accuracy: With an IMS, the chances of human errors in tracking and managing inventory reduce significantly. Automated systems create more reliable and accurate data as compared to manual processes.
Cost Savings: In reducing stock levels and minimizing wastage, companies save on the costs associated with carrying inventory and the expensive ramifications of stockout situations. Thereby, this adds up to the huge savings and higher profit.
Improved Efficiency: Automating inventory processes saves both time and effort compared to manual tracking and management. This streamlines operational efficiency and allows resources to be reallocated to essential tasks.
More Accurate Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting allows organizations to maintain optimal levels of stock so as not to overstock or find themselves in stockout situations. This way, companies are able to meet customer demands without incurring excessive inventory costs.
Improved Visibility: With real time visibility on the state of inventory, businesses can take more informed decisions regarding stock levels, order management and supply chain efficiency. This results in more effective planning and use of resources.
Better Customer Satisfaction: An IMS helps improve customer satisfaction and loyalty by ensuring that products are available when customers need them. Timely execution of orders and timely updates of accurate inventory information make the overall customer experience smoother and better.
•Improved Reporting and Analytics: In-depth reports and analytics offer valuable insights into inventory performance, trends, and room for improvement. It allows them to make data-driven decisions for inventory optimization.
Difficulties in Development of an Inventory Management System
Challenge 1: Cost of Implementation Implementing an IMS can be expensive, particularly for small businesses. Software, hardware, and training costs can be a big investment upfront.
Integration with Existing Systems: It can be difficult to integrate an IMS with existing systems, such as ERP or accounting software. The transition could be difficult due to compatibility issues and migration of data.
Change Management: Moving from manual processes to an automated IMS means changes in workflows, as well as in employee roles. Resistance from employees may arise, necessitating the implementation of effective change management strategies.
Data Accuracy: The IMS’s success depends on the accuracy of the data. Incorrect data can cause wrong inventory levels, stockouts and overstock problems.
You should also regularly schedule maintenance and updates to ensure that your IMS continues to run consistently. This consists of software upgrades, hardware repairs, and constant employee training.
Inventory Management Best Practices
Real-Time Tracking Technology: Real-time tracking can be implemented to track movements and levels of inventory. This ensures real-time and precise information for improved decision-making.
Use Technology: Utilize barcode and RFID technology to help minimize these inaccuracies by automating the inventorying process. This helps improve accuracy and efficiency in inventory tracking.
And combat lost sales, you may want to Optimize Stock Levels: Implement demand forecasting and replenishment planning to keep optimal stock levels on your product. This helps avoid stockouts and overstock scenarios while lowering carrying costs.
Data Accuracy: Conduct regular audits and reconciliation of your inventory data. This ensures discrepancies can be noted, and problems fixed quickly.
Train Employees: Make sure your employees are well-informed about how to use the IMS and follow inventory management processes. The aim is to train everyone involved in the store with at least the basics of inventory management.
Monitor Supplier Performance: Supplier performance should be monitored, including lead times, in order to help ensure stock is replenished on time and in an efficient manner. Develop healthy relationships with suppliers.
Scheduled Reports and Analytics: Use reporting and analytics data to gain insights into inventory performance and trends. Even do feedback-based data collection on what products are and are not selling.
Seasonal Variations Plan: Anticipate and plan for seasonal variations in demand. Scale FFV Inventory up or down based on when there is a demand for stock.
Emerging Trends in Inventory Management
So, These are some high level high tech trends in inventory management. Such technologies have the potential to improve demand forecasting, stock-level optimization and decision-making, to name a few.
Internet of Things (IoT) is Technology for Real-Time Powered Smart Warehousing. Smart warehousing solutions enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and visibility of inventory management.
Blockchain Technology Blockchain technology enables secure and transparent tracking of inventory across the supply chain. This increases traceability, reduces fraud, and enhances trust between supply chain partners.
Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based inventory management systems can offer flexibility and scalability, as well as real-time access to data. These solutions allow businesses to manage inventory anytime, anywhere.
Inventory management: Automation and robotics are changing the way businesses manage their inventory, from order picking to stock replenishment. These technologies drive efficiencies, lower labor costs and prevent mistakes.